Overview
SuperTA is a desktop application to handle student records for Teaching Assistants and Professors in the School of Computing. The user interacts with it using a CLI, and it has a GUI created with JavaFX.
Summary of contributions
-
Major enhancement: added Tutorial Group and Assignment commands. (Pull Requests #19, #62)
-
What it does: These are commands to manipulate Tutorial Groups and Assignments, including the creation and viewing of these data structures.
-
Justification: This feature is essential in achieving core functionality. It allows teaching assistants to create Tutorial Groups and Assignments, which is key to keeping track of student performance.
-
Highlights: This enhancement affects other commands interacting with these data structures.
-
-
Major enhancement: improved User Interface (UI) (Pull Requests #73, #92, #135)
-
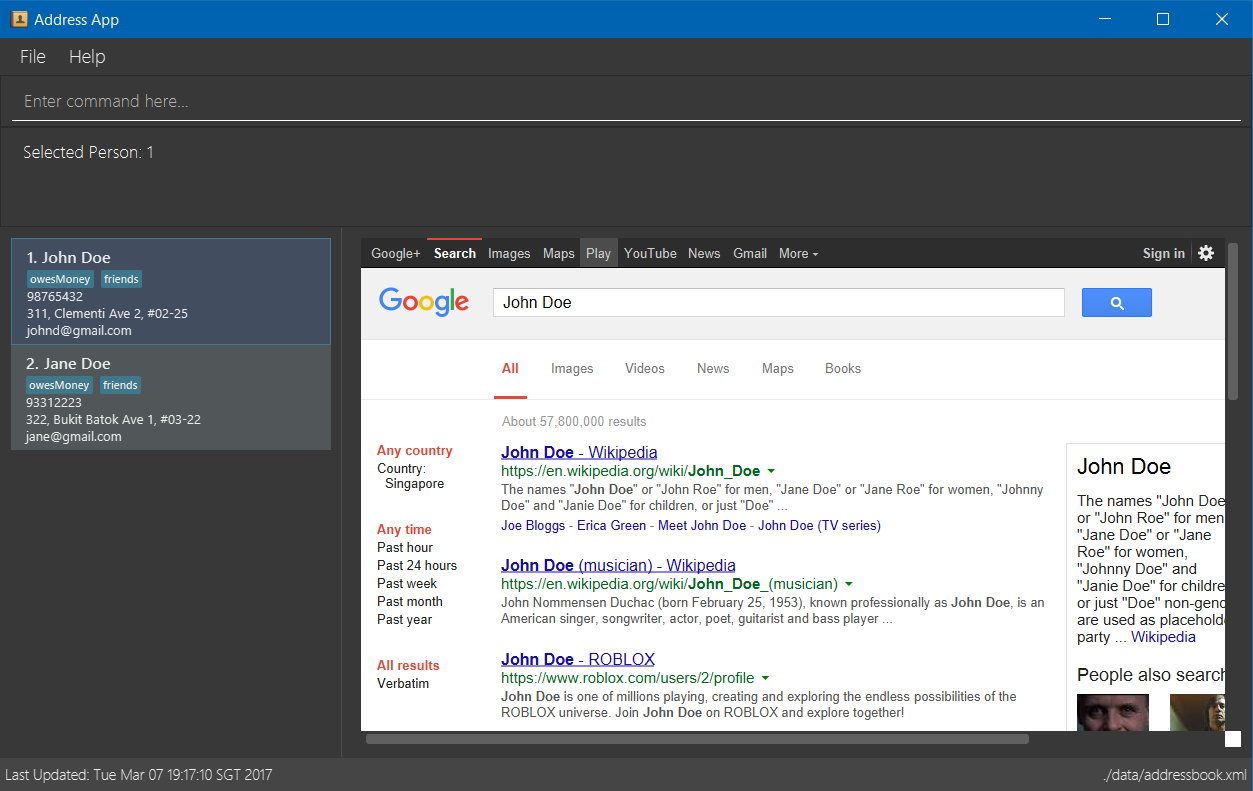
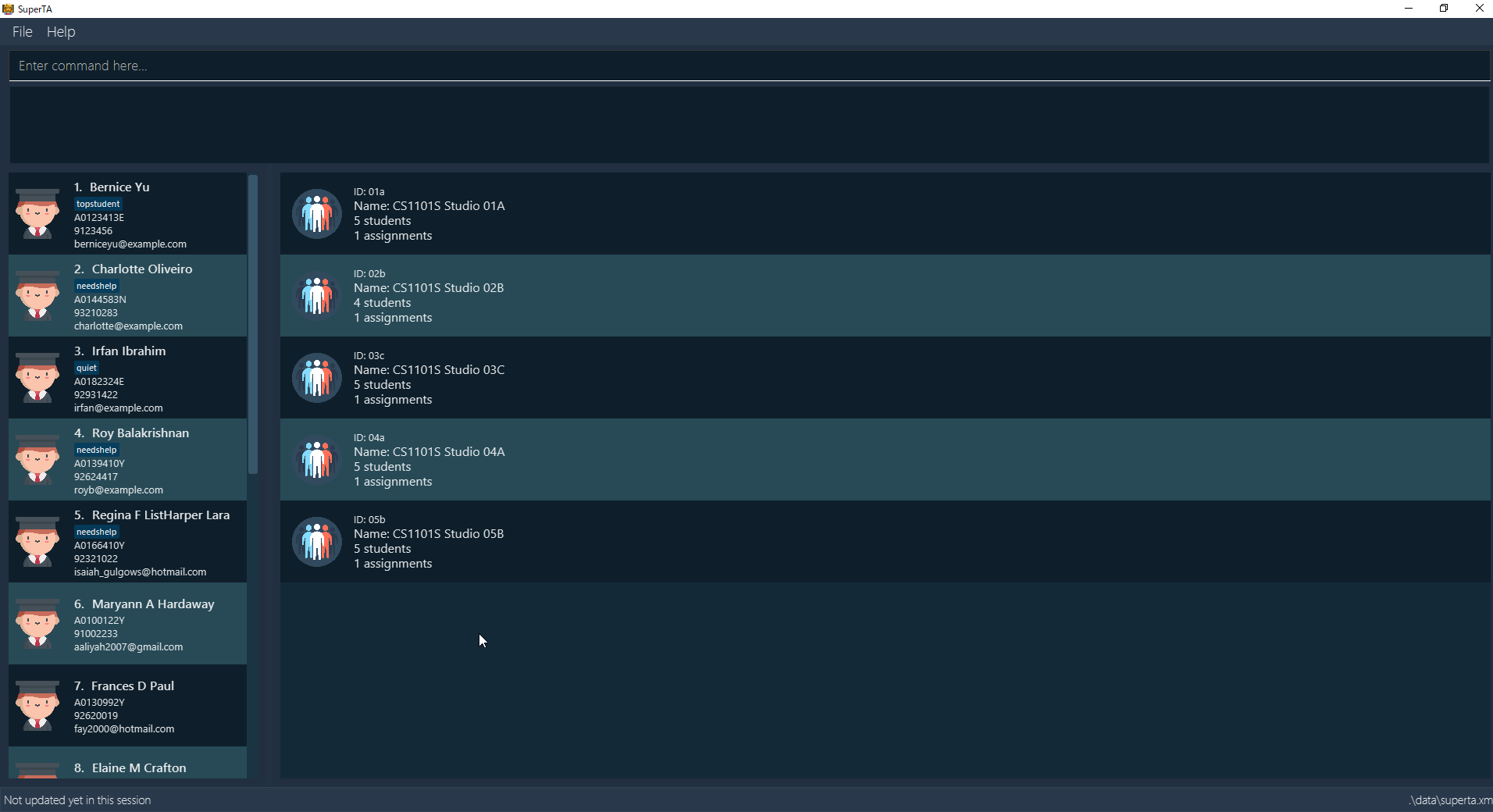
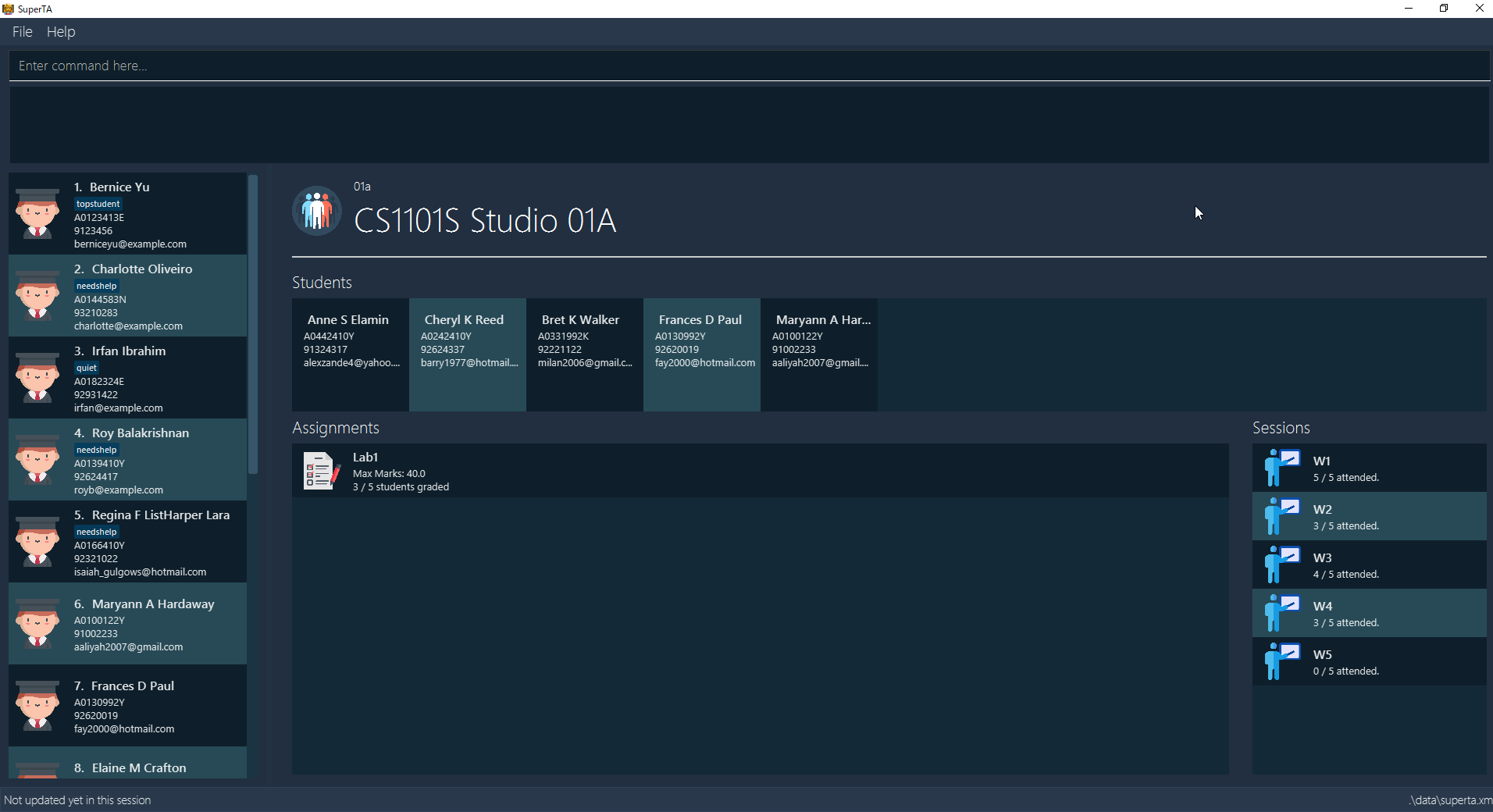
What it does: The user interface was very bare-bones at the start and was not visually appealing. The improvement to the UI makes for a better experience for the user on the whole. The UI was also further improved to display details of tutorial groups, assignments, attendance sessions, as well as students. A few UI event triggers have also been implemented.
-
Before |
After |
|
|
-
Minor enhancement: Added various view commands such as
view-sessionandlist-tutorial-groupswhich will trigger display relevant information in the User Interface. -
Code contributed: RepoSense collated code
-
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Team Lead
-
Managed Project release from
v1.1throughv1.4on GitHub -
In charge of merging most Pull Requests on GitHub
-
Non-trivial reviews for many Pull Requests from team members.
-
-
Enhancements:
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Listing all tutorial groups: list-tutorial-groups
Shows a list of all the tutorial groups, and reflects it on the UI.

Format: list-tutorial-groups
Creating a Tutorial Group: create-tutorial-group
Creates a tutorial group with specified name and ID.
Format: create-tutorial-group n/TUTORIAL-GROUP-NAME id/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID
Examples:
-
create-tutorial-group n/CS1101S Studio 04A id/04a
Creates a tutorial group namedCS1101S Studio 04Awith the identifier04a. -
create-tutorial-group n/CS2103T id/04b
create-tutorial-group n/CS2103T id/04b
Creates a tutorial group named CS2103T with the identifier 04b and a second tutorial group with the same name and identifier04b-dusty123.
Updating a Tutorial Group: update-tutorial-group
Updates a tutorial group’s name.
Format: update-tutorial-group id/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID n/TUTORIAL-GROUP-NAME
Examples:
-
update-tutorial-group id/04a n/CS2103T Tutorial Group 9
Updates the tutorial group with the ID04ato have an updated name ofCS2103T Tutorial Group 9.
View Tutorial Group: view-tutorial-group
Views a tutorial group’s details.
The UI should show this screen:
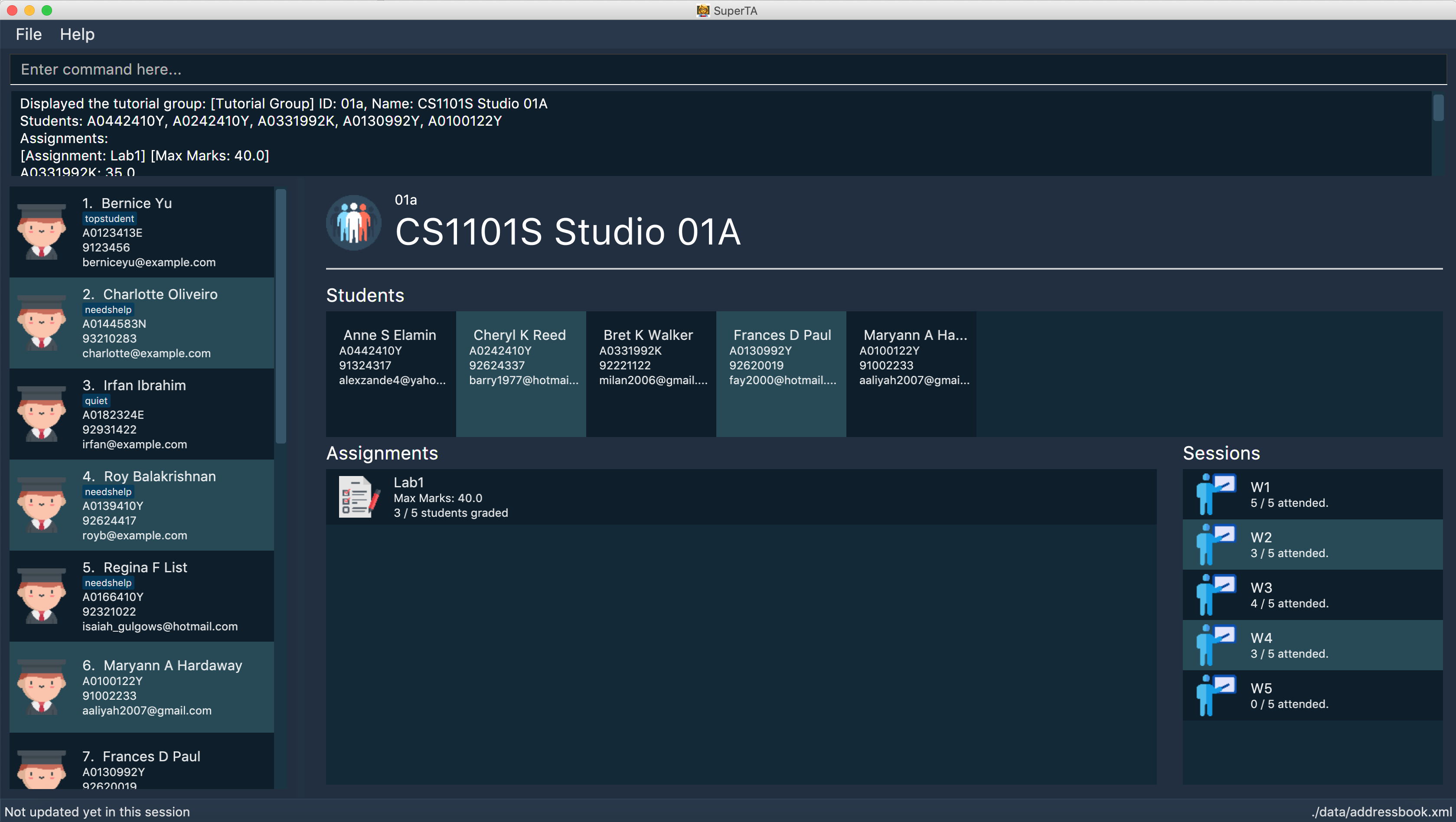
Format: view-tutorial-group id/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID
Examples:
-
view-tutorial-group id/04a
Displays the04atutorial group’s information .
Add to Tutorial Group: add-to-tutorial-group
Adds a student to a tutorial group.
Format: add-to-tutorial-group tg/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID st/STUDENT-ID
Examples:
-
add-to-tutorial-group tg/04a st/A1231231Y
Adds the student with student IDA1231231Yto the tutorial group with an ID of04a.
Creating an Assignment: create-assignment
Creates an assignment for a specific tutorial group.
Format: create-assignment tg/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID n/ASSIGNMENT-TITLE m/MAXMARKS
Examples:
-
create-assignment tg/04a n/lab1 m/40
Creates an assignment namedlab1for the tutorial group with an ID of04a, with the maximum marks for this assignment as40.
Grade Assignment for Student: grade
Enters a grade for a student for a specific assignment in a tutorial group.
Format: grade tg/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID as/ASSIGNMENT-TITLE st/STUDENT-ID m/MARKS
Examples:
-
grade tg/04a as/lab1 st/A0166733Y m/40
Creates a grade with marks40for the student with an ID ofA0166733Yin the tutorial group04afor the assignment with titlelab1.
View Assignment Details: view-assignment
Views an assignment details.
The UI should show this screen:
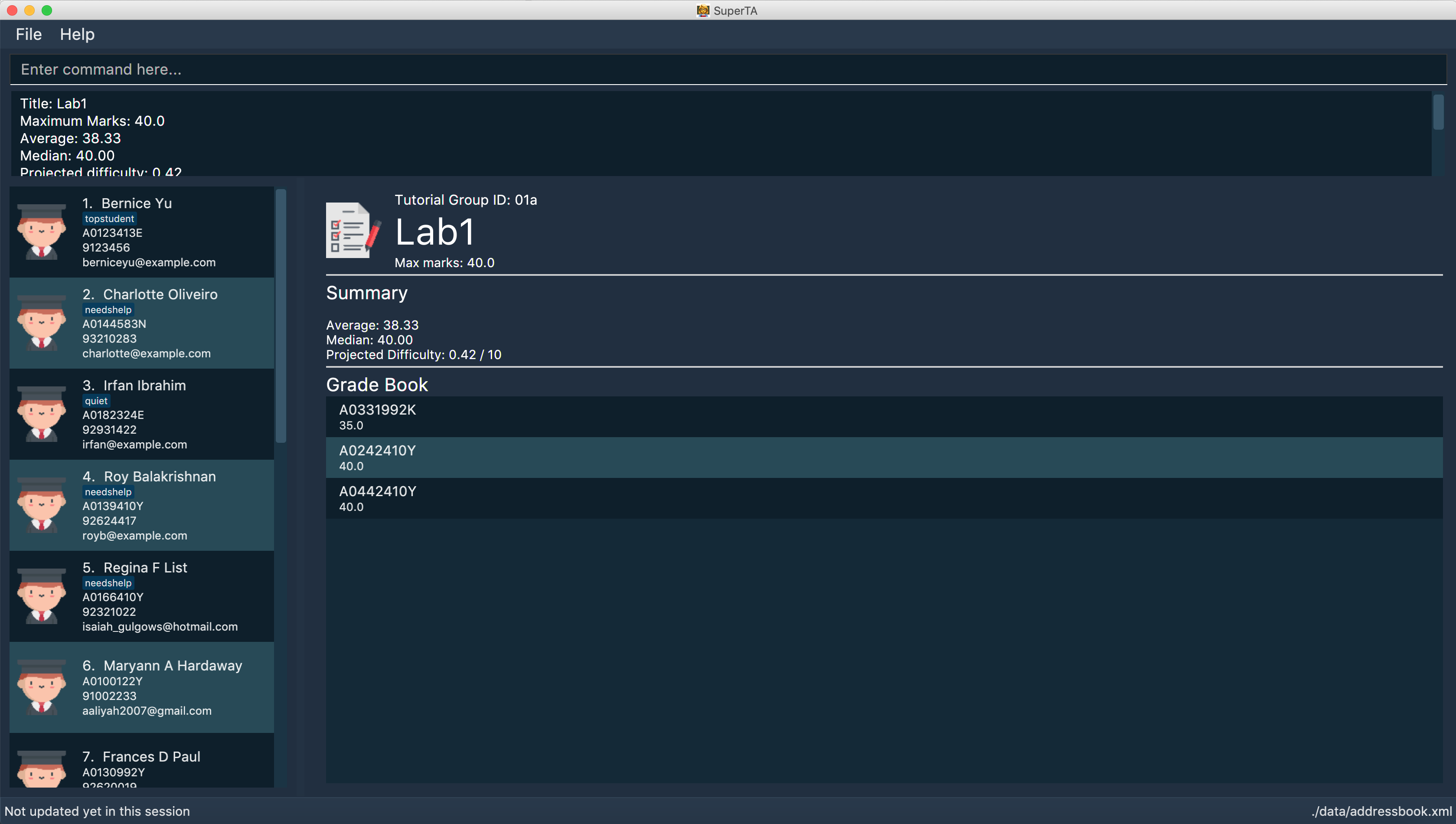
Format: view-assignment tg/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID as/ASSIGNMENT-TITLE
Examples:
-
view-assignment tg/04a as/lab1
Views the assignment details for thelab1assignment in the04atutorial group.
View Attendance Session: view-session
Views the session details for a particular attendance session in a tutorial group.
The UI should show this screen:
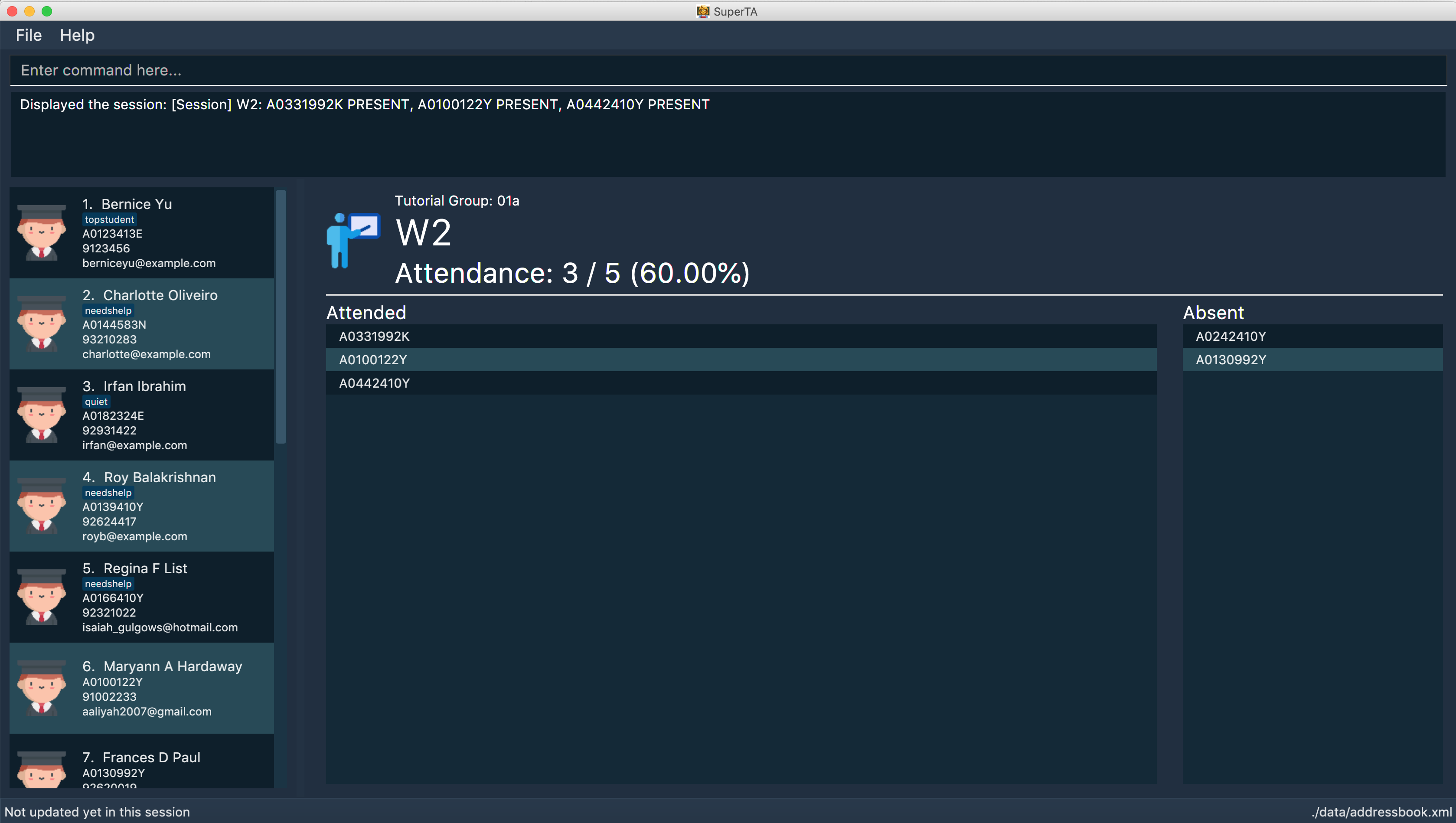
Format: view-session tg/TUTORIAL-GROUP-ID n/SESSION-NAME
Examples:
-
view-session tg/04a n/W1Tutorial
Views the details of the sessionW1Tutorialbelonging to the tutorial group04a.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
TutorialGroupMaster Design
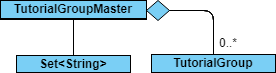
API : TutorialGroupMaster.java
The TutorialGroupMaster,
-
stores all Unique Identifiers (UIDs) of
TutorialGroupin aSet<String>. -
stores all
TutorialGroupinstances that are present in the SuperTA client in aMap<String, TutorialGroup, which maps the ID of theTutorialGroupto the instance for fast lookup. -
exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<TutorialGroup>that can be 'observed', mirroring changes to the internal map. -
Can propogate removal of
Studentinstances to allTutorialGroups. -
does not depend on any other component to operate.
|
The |
The TutorialGroupMaster is able to handle lookup of TutorialGroup by ID quickly because it stores TutorialGroup instances in a Map which has the TutorialGroup IDs as key values. This notion of a master is necessary so we can handle operations such as propagating Student deletions to every single TutorialGroup.
TutorialGroup Model

API : TutorialGroup.java
The TutorialGroup model,
-
has a unique identifier.
-
has a name.
-
has a list of
Students that belong to it. -
has a list of
Assignments that belong to it. -
has a list of
Sessions that belong to it. -
should only contain
Students that are in the main client.
|
The |
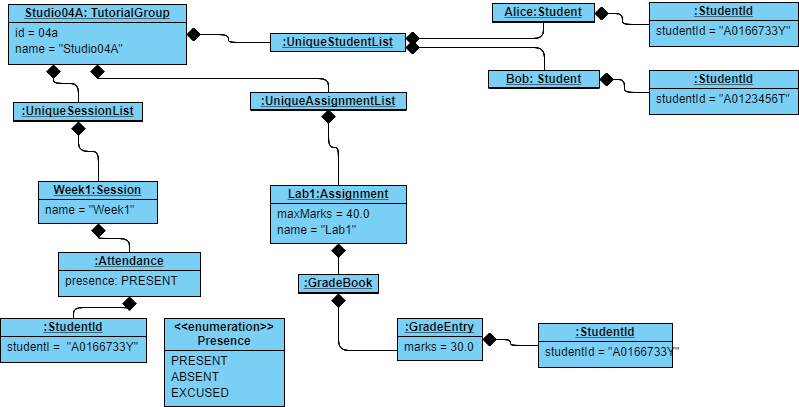
This is an example of the use case of a TutorialGroup. In this object diagram, we have a TutorialGroup with the name Studio04A and the ID 04a. It holds lists of Student s, Assignment s, and Session s in its appropriate lists. Each entity is not coupled with each other - it uses the StudentId to find out which Student is associated with it. For example, The GradeEntry object composes of a StudentId object, which will allow other components to find out which is the underlying Student model with this StudentId. This is done so that we don’t have to update each entity with updated copies of a Student when the user triggers an update event.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Alternative Implementation Methods
-
Alternative 1: Store
Assignments,Sessions, andStudents in a normalised manner - that is, theModelManagerwould instead contain lists of all of these entities. EveryTutorialGroupwould then reference an identifier if it wanted a reference to that entity.-
Pros: Any updates to an underlying model would be propagated to every
TutorialGroupreferencing it. Normalised data is also easier to reference. Future classes can also reference these with no problem. -
Cons: This implementation will require additional layers of abstraction, and will require many changes to the model.
-
Creating a Tutorial Group
-
Creating a tutorial group
-
Prerequisites: List all tutorial groups using the
list-tutorial-groupscommand. -
Test case:
create-tutorial-group id/04a n/Test
Expected: A new tutorial group with the id04aand the nameTestis created, and the list view is updated. -
Test case: Duplicate ID -
create-tutorial-group id/04a n/Test
In this test case, theidargument has to be anidthat already exists in the memory. For example, you can run the above test case with the exact same arguments again. Expected: A new tutorial group with a different ID is created. The new ID has a random suffix appended to it. For example, if you runcreate-tutorial-group id/04a n/Testtwice, the second tutorial group will have an ID that looks like04a-stormy492.
-
Deleting a Tutorial Group
-
Deleting a tutorial group
-
Prerequisites: Have a tutorial group with an ID of
04ain the memory.
View the tutorial group using theview-tutorial-group id/04acommand. -
Test case:
delete-tutorial-group id/04a
Expected: The tutorial group is deleted. The UI shows[Deleted]next to the tutorial group name.
-
Grading a student
-
Grading a student
-
Prerequisites: Have one tutorial group with an ID of
04a, and an assignment that belongs to it with the namelab1with a maximum mark of40.0. Also, a student with a student ID ofA0166733Yshould be added to the tutorial group.
View the assignment in the tutorial group using theview-assignment tg/04a as/lab1command. -
Test case:
grade tg/04a st/A0166733Y as/lab1 m/35.0
Expected: The student gets graded35.0out of40.0marks. If you are in the detailed tutorial group or assignment screen, the UI should be updated accordingly. -
Test case:
grade tg/04a st/A0166733Y as/lab1 m/40.1
Expected: An error message should be shown in the status message, because40.1is greater than the maximum marks oflab1. -
Test case:
grade tg/04a st/A0166733Y as/lab1 m/-1
Expected: An error message will be shown, since negative marks are invalid. -
Test case:
grade tg/05a st/A0166733Y as/lab1 m/30
Expected: An error message showing that there is no such tutorial group. -
Test case:
grade tg/04a st/A0123456T as/lab1 m/30
Expected: An error message showing that there is no such student in this tutorial group. You can also try this when there is a student in the main directory with this ID, but this student is not added to the tutorial group. -
Test case:
grade tg/04a st/A0166733Y as/lab2 m/30
Expected: An error message showing that there is no such assignment.
-